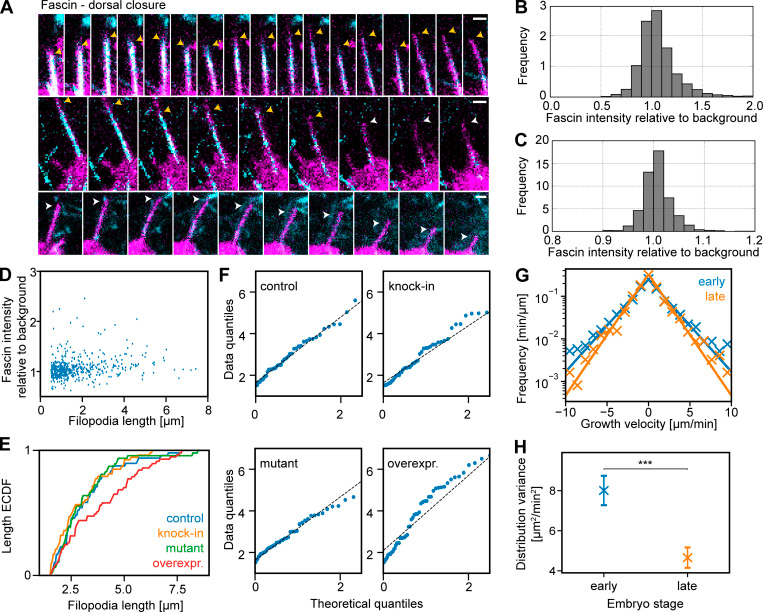
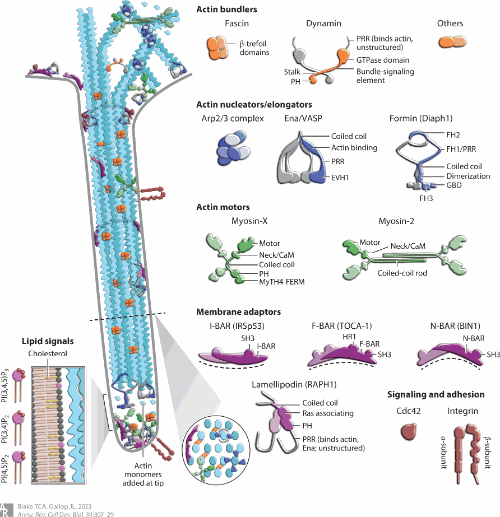
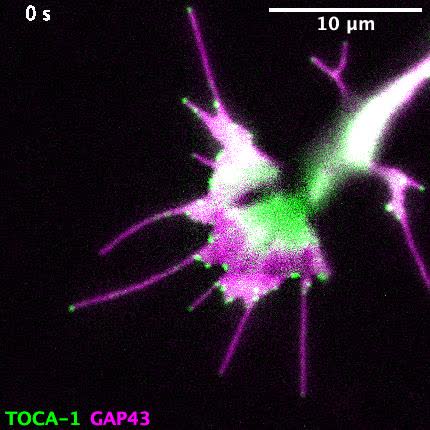
Dobramysl et al analyzed the localization of actin regulators within filopodia in Drosophila embryos and in an in vitro system of filopodia-like structures (FLSs), finding that the composition of the regulatory protein complex where actin is incorporated (the filopodial tip complex) is heterogeneous both in vivo and in vitro. Different pairs of proteins correlate with each other and with actin bundle length, suggesting the presence of functional subcomplexesnconsistent with a theoretical framework where three or more redundant subcomplexes join the tip complex stochastically, with any two being sufficient to drive filopodia formation.